Review Process
Review Process
The IJABR applies a double-blind peer-review process. The author(s) and the reviewers of the submitted manuscript remain anonymous in order to guarantee the impartiality and fairness of the review.
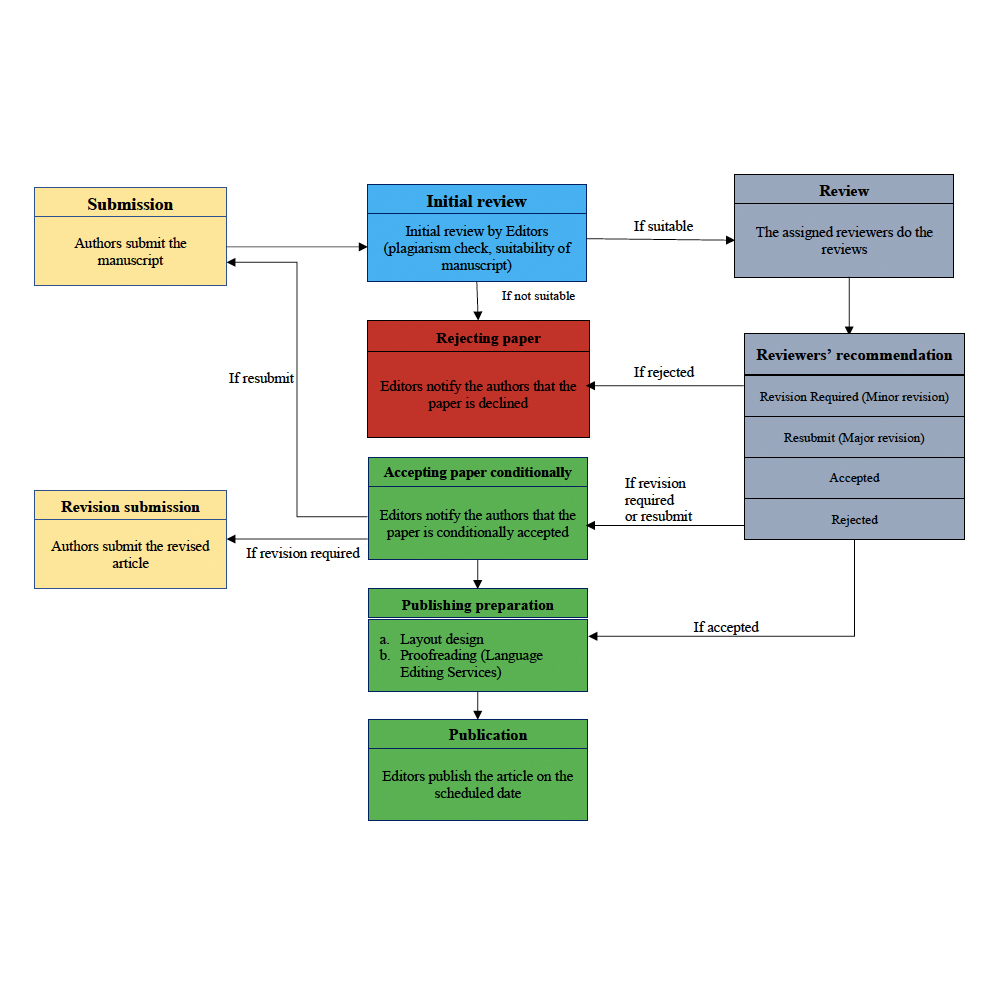
First, submitted manuscript are initially reviewed by the editor to verify: (1) no plagiarism exists, (2) the suitability of the manuscript (topic and template). A manuscript that is considered unsuitable will be rejected, while the suitable ones (author(s) personal contact information removed) are sent to two independent reviewers for further assessments.
There are four types of recommendation reviewers can make:
- Revision required indicates the submission requires minor revisions. This requires the authors to revise and re-submit the manuscript within a limited time.
- Resubmit means the submission requires major revision. The authors can resubmit the improved manuscript as a new manuscript.
- Accepted means the manuscript can be published directly.
- Rejected means the manuscript is not suitable to be published in the IJABR.
Based on the reviewers’ recommendation, the Editor in Chief will make a final decision for the manuscript. For any accepted manuscript, the author will receive the Letter of Acceptance and must submit the Copyright Transfer Agreement via the IJABR system.
Reviewer Guideline
Components and evaluation indicator of reviewers assessment are described in the following Table:
|
No |
Component |
Evaluation Indicator of reviewer(s) |
|
1 |
Title |
Effective, specific, and clear |
|
2 |
Abstract (in English) |
Complete description of the essence of the manuscript |
|
3 |
Keywords |
Search terms representing the essential concepts of the manuscript |
|
4 |
Introduction (background, Objective or scope, literature review) |
Importance, timeliness, originality, and relevance of the topic, and compatibility of these with the clear and specific research objectives |
|
5 |
Methods |
Accurate, specific, and clear |
|
6 |
Results (Analysis and Synthetic) |
Complete and consistent reporting and explanation of results |
|
7 |
Discussion (Interpretation) |
Timeliness of findings, relevance to extant research, and evidence-based contribution of findings and ideas to the development of scientific enquiry |
|
8 |
Conclusion |
Logical, valid, brief, and clear |
|
9 |
Suggestion |
Practical actions, for further development of theory and its application |
|
10 |
Bibliography |
Timeliness and quality of the primary references. Rules: at least 90% of the primary journal articles related scientific research has been published within the last ten years. |
